Security tools such as I2P, Tor, VPN, and Proxy are the most preferred in an era of such privacy hassles. These provide more or less the same security features with different intensities. Tor vs. VPN means that you can hide your IP address, unblock restricted websites, and encrypt your traffic through both techniques.
Meanwhile, I2P vs. proxy answers that you can hide your IP address and surf the web anonymously.
However, certain conditions make all of them different; one is preferable to the other. Here, we highlight the marking differences between Tor and VPN, I2P, and proxy, making it easy for the readers to decide which one to choose.
How all of these technologies work
Not all Internet users know the working patterns of Tor, VPN, I2P, and Proxy. By understanding this, it would be easy for the readers to figure out the advantages and disadvantages discussed later in the article. However, those familiar with their functions could skim through it and jump on the section explaining Tor VS VPN and I2P VS Proxy.
TOR (TOR Network)
Tor is software that allows you to surf the internet anonymously. Without any charges, it downloads from the internet. The Tor browser works differently from a VPN. The data encrypts with various nodes. The three servers or nodes are kept between your connection and the destinated location to provide better anonymity.
With each passing node, the data is encrypted. Whereas nodes to which data transfers are just aware of the location to which it will transfer the data and from where it is coming. Therefore, the whole route, the origin of the data, and the destination of that data remain anonymous.
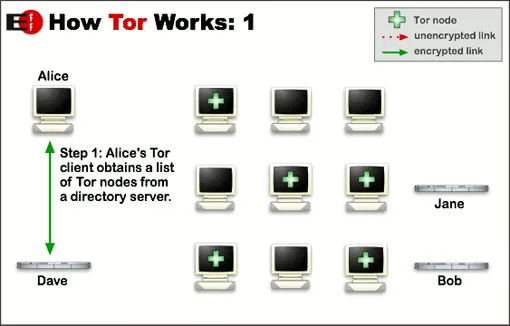
The Tor network’s relay circuit is reset after every 10 minutes. In this way, you can see the previous action tracks easily.
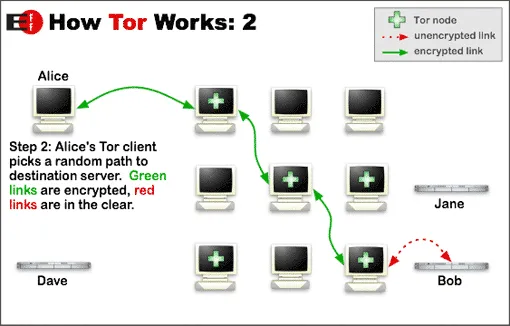
The nodes operate by different volunteers. Thus, the more significant number of volunteers makes the network more efficient.
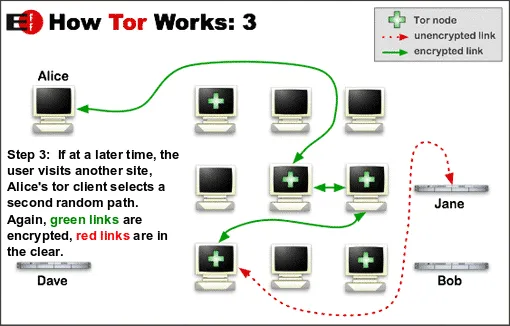
Therefore, it is difficult for the NSA to de-anonymize a Tor user by relating the chain to the origin point. Tor also stops middle-men snooping, such as ISP tracking or other cyber goons with malicious intent.
Your data is vulnerable when it reaches the last server where the decryption occurs. An operator at the previous server could read all this information and use it for any such malicious purpose. Therefore, you should use HTTPS while sending your personal data so that it remains encrypted.
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
VPNs are a much-known term to internet users of the present age. A security technology getting immense acknowledgment and consideration is a Virtual Private Network (VPN) due to some of its robust privacy features.
Your internet traffic encrypts through a server. For instance, if you visit a website while connecting to a VPN service, it will go to a server and then to the web page. This process of encryption provides many advantages for your data security.
Encrypting traffic means a person between you and the server could not get your data. When an internet provider or any other entity looks down at the encrypted data, it appears as an inappropriate juggled text which is unrecognizable.
Also, a VPN service lets you get over the geo-restrictions through encryption. For example, if you are present in Beijing and the VPN server you are connecting to is in the US. Then the site you visit will think of you as a resident of the United States. Therefore, you can stream content blocked or restricted in Beijing that is available for the US citizens, such as Netflix, HULU, etc.
However, using a VPN makes your data visible to the VPN servers for which most VPN providers claim their zero-logging policy. But you never know whether this is a genuine promise and whether this policy will remain the same. So, a VPN could also reveal your data, especially to the state actors who are more likely to compel VPN providers to break their rule.
I2P Anonymous Network
The I2P, or Invisible Internet Project, is a devolved anonymizing network. It builds by using Java on similar grounds to Tor. I2P is effectually an internet within an internet.
If you connect to this network, you can quickly send emails, surf websites, use blogging and forum software, host websites, benefit from devolved file storage, indulge in anonymous real-time chat, and many more. Moreover, you can comfortably browse the open web anonymously.
Unlike other anonymizing networks, I2P doesn’t try to provide anonymity by hiding the creator of some communication while not the recipient. The peers use I2P to communicate with each other anonymously. In this network, the sender and receiver are unrecognizable to each other and third parties.
A set of nodes or routers makes the I2P network. It also contains numerous unidirectional inbound and outbound virtual paths. A cryptographic knows every node. The nodes communicate with each other through transport mechanisms such as TCP and UDP, which pass several messages.
The client applications have their destination or cryptographic identifier, allowing for sending and receiving messages. The clients are free to connect to any router and approve the temporary lease of some tunnels. These tunnels use for transmitting and receiving signals by the network.
I2P possesses its internal network database to distribute routing and contact the information firmly.
I2P network offers several advantages to users. It shares files at a faster rate. Moreover, there are no timing attacks and Man in Middle Attacks. But it also imposes certain risks too. The I2P network doesn’t guarantee anonymity when using it in public.
Moreover, it works perfectly when used within the correct specifications. The I2P network does not work on the typical user with a Windows or Mac system. You can use Linus OS to confirm helpful anonymity.
Proxy Service
A proxy is like a gateway between the user and the internet. It acts as an intermediary server dividing the end users from the website they surf. Proxy offers different levels of security, privacy, and functionality subject to your need, use, or organization policy.
When using a proxy service, internet traffic data runs through the proxy server to address your request. The request we brought back to the same proxy server. Later the proxy server onwards the data obtained from the website.
A proxy server is nothing but a computer on the internet. The IP address is already known to your computer.
The web request first goes to the proxy server. Later the proxy server on your behalf makes a web request. Moreover, the proxy server collects the response from the web server and forwards the web page data. In this way, you see the page within your browser.
It should be remembered that when the proxy server forwards the web request, it may change your data and get you the information you suppose to see.
A proxy server is capable of changing your IP address. It hides the IP address but is unable to encrypt data. Also, a proxy server can block access to specific web pages depending on their IP address.
Tor vs VPN: What is the main difference
With the same core functionality, anonymity, both security technologies are effective in different circumstances. Also, the usage for both VPN and Tor differs from each other.
Streaming
For streaming purposes, you want to bypass geo-restrictions. Most countries put these restrictions on the content of other nations. Tor VS VPN for such use is the same in providing anonymity; however, speed is the most critical thing while streaming content. Therefore, it is a pronounced judgment that a VPN has the edge over Tor concerning speed.
Many Tor users complain of languid speed, an extreme annoyance for those viewing content. Streaming content with a flawed speed is harrowing, especially when popular content such as Netflix, Hulu, HBO, and others are massive streaming channels.
Anonymity
If you require high anonymity, then a Tor browser could be a better option than a VPN. Because of many nodes and diverged networks, it is difficult for the state actors such as governments and law enforcement agencies to track the origin of data.
Torrenting
Torrenting is an act that has strict rules in most countries. They are difficult to understand for most people. However, you could safely do torrent downloads and P2P file sharing using technologies such as Tor and VPN.
But the question here is, among VPN and Tor, which one is more efficient while torrenting? Heavy media content, such as HD movies, takes a long time to download. Tor being a relatively slow service makes it more time-consuming as it consists of many nodes. Therefore, torrenting could be faster and more secure with a VPN service.
Privacy & security
We have highlighted many aspects in which one has the edge over the other. But looking forward to the overall impression generated by these aspects of Tor and VPN. It could be said that Tor is better to use when you want anonymous browsing. However, VPN serves many features such as spoofing geo-restrictions, anonymity, torrenting, faster streaming, and security from hackers.
Although, it is recommended to choose the best VPN services that are trusted by Internet users and are effective for their services.
I2P VS Proxy: What is the main difference
Both I2P and Proxy provide anonymity to the users in different circumstances. These differences are discussed below:
Streaming
Streaming is associated with speed. The proxy works at a much faster speed than I2P. If you are using a proxy server, then there is no chance that your internet connection will slow down. However, I2P works at a slower speed and therefore is not a good option for streaming.
If you have to choose between I2P and a Proxy for streaming, then it is recommended to use a Proxy server.
Anonymity
Both I2P and Proxy provide different levels of anonymity to the users. If you want to surf the web anonymously by hiding your actual IP address, then you can go with a Proxy. However, if you want to anonymously surf the Dark web or any other private web, you should choose the I2P network.
Privacy and security
Both tools provide different levels of privacy and security.
A proxy server does not offer an encryption facility but efficiently hides users’ IP addresses. I2P effectively encrypts the internet traffic data but fails to encrypt the network activity.
Therefore, Proxy provides privacy and security by hiding the actual IP address, while I2P provides security by encrypting the data.
I2P vs. Tor
Both I2P and Tor perform differently under different circumstances:
Streaming
While I2P doesn’t perform at the top levels in terms of speed, it is still faster than TOR, making it a better choice for streaming. Tor is usually slow due to its infrastructure. When streaming, your data has to travel across multiple nodes, which reduces connection speed in the long run. However, this is not the case with I2P.
Also, unlike TOR, designed for secure web browsing, the I2P network was initially designed to share files. It has a higher performance and better streaming speeds than TOR.
Anonymity
The Invisible Internet Project (I2P) and The Onion Router (TOR) are renowned as anonymous proxy networks, frequently utilized by various dark web sites such as Agora Marketplace. I2P was created with Java concepts and operated on a distributed peer-to-peer framework. One of the critical aspects of I2P is its adherence to the API design feature, which enhances anonymity.
TOR, on the other hand, was designed to browse the visible internet secretly. It uses a centralized directory-based model to manage and supervise its network. This centralized structure enables TOR to gather and report web usage statistics.
Three distinct types of nodes are involved within the TOR network: internal relays, directory servers, and exit points so when you connect to the TOR network, your internet traffic hops between various relays before reaching its final destination via exit nodes.
Privacy and security
I2P is a more secure alternative to Tor in many aspects. It addresses some of the significant vulnerabilities found in the Tor network, like malicious exit nodes, timing analysis, and the likelihood of DDoS attacks.
However, I2P is not as user-friendly as Tor since it is limited to applications and websites specifically designed for the I2P network. This restriction means I2P is primarily used for email, torrenting, IRC, and deep web access.
In these specific contexts, I2P offers a high level of anonymity. On the other hand, Tor has a broader range of use cases but is accompanied by significant flaws. To enhance your privacy, using a VPN independently or in conjunction with Tor is advisable.
Onion Routing vs. Garlic Routing
Tor employs onion routing as its technique, which involves adding multiple layers of encryption to a message, resembling the layers of an onion. As the message traverses through each node, these layers are gradually removed, leading to a decrypted message at its destination.
This process intends to ensure that the message’s contents remain hidden from any intermediaries between the sender and the exit node. However, a notable vulnerability in this approach is known as ‘timing analysis’. This involves an attacker comparing the timing and size of messages across different devices to link them together.
To illustrate, imagine you are using Tor to send a message to another individual. While your Internet Service Provider (ISP) may be unaware of the message’s contents, they can still log all your traffic.
By cross-referencing this information, the ISP can deduce that anonymous traffic left your device and reached the recipient based on matching package sizes and timings. To address this weakness, garlic routing emerges as a solution. It combines multiple messages which travel through the I2P nodes before being revealed at the final destination and forwarded to their respective delivery addresses.
This bundling of messages makes it more challenging to perform traffic analysis on individual users since their packages are intertwined with those of other individuals and applications.
Which one is better for streaming?
VPN is a better option than Tor, Proxy, and I2P. The VPN service rarely slows down and thus is known best for streaming.
Tor works at a languid speed, so data is casually bounced by many nodes, each of which can be present anywhere in the world. Therefore, using Tor is painful as its speed is slow and takes much time to stream.
Whereas I2P works a little faster than Tor. Tor is full of unrevealed services, many much faster than Tor-based equivalents. However, a proxy does not slow down the internet. But it can make the internet connection feel slower; thus, it is a better option than Tor and I2P but not better than VPN.
Which one provides better anonymity?
You must use a proxy service if your primary concern is only hiding your IP address.
However, if you want private access to hidden services and messaging techniques within a distributed network of peers, you should choose I2P.
If you wish to encrypt all your internet traffic and don’t want to compromise on the speed, too. Thus, VPN is the best option for anonymity. But to access private sites and the dark web, you should use the speed and choose Tor.
Which one provides better security and privacy?
All of them provide better security and privacy in one way or another, with some variations.
VPN protects users’ privacy by hiding the IP address and encrypting the internet traffic. However, various free VPN providers do not always provide users with security and privacy.
Similarly, I2P protects privacy until you’re using it on regular web browsing. It encrypts the data but does not encrypt the network activity of the system.
Tor provides better security and privacy in all aspects. While using Tor, no one is going to identify you anywhere. While proxy also hides the IP address, the protection level is less than Tors.
We hope you are now fully aware of the main differences between Tor Vs. VPN and I2P Vs. Proxy and can decide which tool is the most secure one.
Share this article
About the Author
Rebecca James is an IT consultant with forward thinking approach toward developing IT infrastructures of SMEs. She writes to engage with individuals and raise awareness of digital security, privacy, and better IT infrastructure.
More from Rebecca JamesRelated Posts

10 Best Alternatives of Tunnelbear (Free and Paid in 2024)
KEY TAKEAWAYS If you have decided not to use TunnelBear VPN, then the following VPN providers will i...

4 Best Ways to Stop ISP Throttling Enjoy Fast Speed in 2024
KEY TAKEAWAYS If you’re experiencing ISP throttling, using a VPN is the best method to prevent...
How to Hide Your IP Address? 7 Best Ways
KEY TAKEAWAYS Masking your IP address is necessary to protect yourself from multiple cyber threats. ...

What is a VPN Kill Switch and How Does it Work?
Numerous internet users have now observed the possible risk of online data exposure to ISPs or cyber...

Does VPN Slow Down Internet Speed? [Resolved]
KEY TAKEAWAYS A VPN connection indeed reduces your speed because of encryption protocols. It routes ...

Why Should You Use a VPN? 12 Best Reasons
KEY TAKEAWAYS As almost everyone has nowadays access to the internet, more cyberattacks are taking p...





